NEWS
David Seung U Lee and Yu Jin Kim have delivered oral presentations at KoSMI
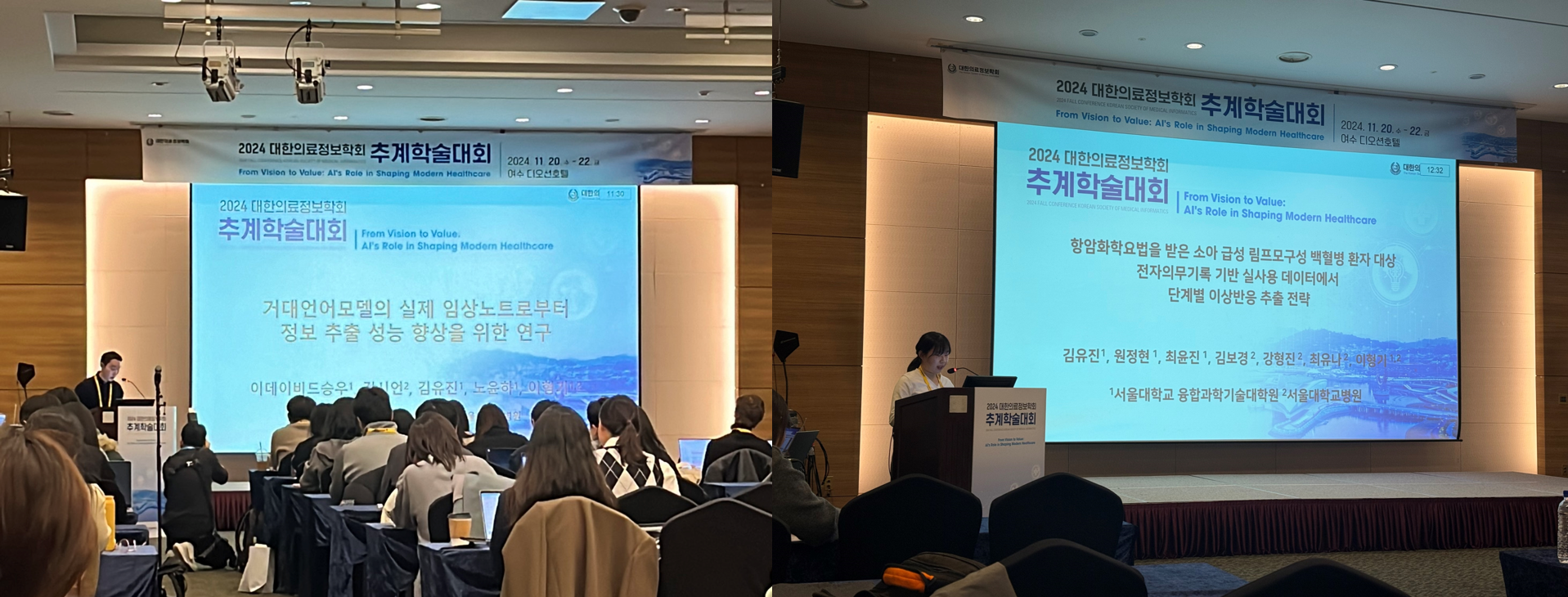



CCADD members attended the 2024 Fall Conference of the Korean Society of Medical Informatics (KoSMI), which was held from November 20th to 22nd at the Ocean Resort in Yeosu.
The event was especially meaningful because David Seung U Lee and Yu Jin Kim delivered oral presentations there.
The theme of this year’s conference was "From Vision to Value: AI's Role in Shaping Modern Healthcare." It focused on how artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping the future of healthcare and transforming itself from a mere vision into tangible value. The discussions delved deeply into AI's roles in this transformative process. The conference provided a platform to share the latest research achievements and explored how AI contributes to patient care and system improvement in real-world medical settings.
As for the oral presentations by our members, David Seung U Lee presented the study entitled “Improving Few-shot Performance of Large Language Models to Extract Clinical Information from Real World Clinical Notes.” His research addressed the challenges of extracting information from unstructured and noisy clinical notes using large language models (LLMs). The study proposed a cost-effective strategy to enhance LLM performance by optimizing factors such as model size, example selection, and arrangement strategies. Using 2,110 annotated clinical notes from Seoul National University Hospital, the study demonstrated the trade-offs between prompt design and performance, with optimal results achieved using 15 examples and BM25-based example selection. Additionally, the research explored the impact of data drift on LLM robustness, offering insights into devising better prompting strategies for real-world applications.
Aligned with the focus of the conference, Yu Jin Kim also presented the study entitled “Adverse Event Extraction from EMR-Based Real-World Data in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients Receiving Chemotherapy.” The study introduced a sequential strategy for efficiently extracting adverse events (AEs) from electronic medical records (EMR), combining structured data analysis with minimal manual review. The method effectively captured clinically relevant AEs with reasonable accuracy, demonstrating its potential to enhance real-world data utilization for evaluating treatment safety in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
By CCADD|November 26, 2024
Keywords



CCADD
Center for Convergence Approaches in Drug Development, Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology, Seoul National University
Room C-208, 145 Gwanggyo-ro, Yeongtong-gu, Suwon-si, Gyeonggi-do, 16229, SOUTH KOREA (Gwanggyo)
Room 406, Building 17, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 103 Daehak-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul, SOUTH KOREA (Yeon-gun)
Tel: +82-31-888-9189 (Gwanggyo); +82-2-3668-7381 (Yeon-gun)
Fax: +82-31-888-9575
Email: ccadd.snu@gmail.com